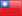
Emerald
Fingerprints of Nature
The vivid brilliance of its colour makes Emerald a unique gemstone indeed. But really good qualities are rare, as inclusions will often spoil the impression - traces of an active history of origin characterising the gemstone. Fine inclusions, after all, do not diminish the value; on the contrary. An Emerald of deep, vivid green with inclusions will be valued higher than an inclusion-free stone of paler colour. Almost endearingly, experts call the many crystal inclusions or fissures which are so typical for this gemstone a "jardin". The tender green plant-like structures in the Emerald garden are considered as identifying characteristics of a naturally grown Emerald.
Where do they come from and why are they acceptable? In order to answer this question we must look back in history over 65 million years to the times when Emeralds were created. From a chemical-mineralogical point of view, Emeralds are beryllium aluminium silicates achieving the good hardness of 7.5 to 8. Like blue Aquamarine, pale pink Morganite, golden Heliodor and pale green Beryl, Emerald is also a member the Beryl gemstone family. Pure Beryl is colourless. Colours only exist when traces of certain elements are added in the process. For Emerald, traces of chrome are mainly responsible for the fascinating colour. These elements usually occur concentrated in the Earth crust at completely different locations from beryllium, and therefore Emeralds should not exist at all. However, in the course of extreme tectonic processes these contrary elements were brought together and created one of our most beautiful crystals in the process of crystallising under enormous heat and high pressure. Due to the tensions involved in the geological conditions there occurred several smaller or larger disturbances during creation. And a view inside the heart of an Emerald, with a magnifying glass or a microscope, will tell us something about the wild and vivid process of creating this unique jewel: there may be smaller or larger fissures recognisable, perhaps there will be a miniature crystal or a small bubble within, and a variety of structures may be discerned. Some of these phenomena had the time to heal out in the growth phase and show the serrated three-phase-inclusions, which are so typical for Colombian emeralds: cavities filled with liquid, often containing also a small gas bubble and tiny crystals.
Obeying the laws of logic, such a history of creation makes it virtually impossible for larger crystals to grow without imperfections. Therefore, then, it is a rare event indeed when a larger emerald of good colour and good transparency is found. And this is why such fine Emeralds are so valuable. But the very fact that Emeralds have a vivid past mean that we like to see traces of this in the stone - provided there is only a fine "jardin" apparent in the stone, and not a wildly overgrown and untamed jungle of a garden, which negatively effects colour and transparency.
The World of Fine Emeralds
Colombia is still the main country of occurrence for fine Emeralds. About 150 mining sites are known there, but not all of these are currently being exploited. The most famous names in this context are Muzo and Chivor, where even in pre-Colombian times the Incas mined Emeralds. The economically most important mine is Coscuez. Estimates ascribe about three quarters of the current Colombian emerald production to the about 60 locations belonging to the Coscuez mine. Colombian Emeralds are set apart from Emeralds of other origin by their especially fine and brilliant green which is not influenced by any bluish tinge. Depending on the place of occurrence, the colour of Emerald may vary. This fascinatingly beautiful colour is highly coveted in the international Emerald trade, so that even visible inclusions which can be discerned with the mere eye are acceptable. But Colombia has more to offer: from Colombian Emerald mines occasionally there come Emerald rarities on the market, like "Trapiche-emeralds" displaying a six-ray-star , or like the extremely rare Emerald Cat's Eye.
Although undoubtedly the best and finest qualities of emeralds are from Colombia, it would be wrong to suppose that the "birthplace" of a stone automatically guarantees immaculate quality. Fine emeralds are also found in other countries such as the Zambia, Brazil, Zimbabwe, Madagascar, Pakistan, India, Afghanistan or Russia. Mainly Zambia, Zimbabwe and Brazil have gained an international reputation for fine Emeralds. From Zambia there are exported excellent Emerald crystals in a beautiful, deep emerald green showing good transparency. Their colour is usually darker than that of Colombian stones and often has a fine bluish undertone. From Zimbabwe's famous Sandawana mines there come usually smaller, but very fine Emeralds in a vivid and deep green, often with a slight yellowish-green shade. Brazil's gemstone mine Nova Era at present even challenges the famous Colombian Emerald mines: their production of Emeralds in beautiful shades of green compete in their attractive beauty with the gemstones offered by the neighbouring country. Because of the occurrences found in Africa and Brazil, Emeralds are fortunately available in larger amounts today than in earlier times - much to the pleasure of their fans.